


A bull market is a period when stock prices generally increase. Bull markets typically last for several years, and there can be multiple bull markets within a decade or a single prolonged bull market.
During a bull market, investors are optimistic about the future and are more confident investing in the stock market. This confidence can lead to increased buying, which drives prices even higher.

A combination of four factors typically leads to a bull market:
Low interest rates make it cheaper for companies to borrow money, leading to increased investing and, ultimately, higher profits. Improving economic conditions means more people are employed and making more money. The extra disposable income can increase consumer spending and drive up stock prices.
Increased corporate profits are also a key driver of bull markets. When companies are doing well, their stock prices tend to rise. This can lead to a feedback loop, where higher stock prices lead to more buying and further price increases.
Finally, bull markets are often driven by investor confidence. When investors feel confident about the future, they are more likely to invest in stocks. This increased demand can lead to higher prices.
When stock prices rise, investors make money by buying and selling them at a higher price. This is the most basic way to profit from a bull market.
Another benefit of bull markets is that companies can raise capital easier. When stock prices rise, companies can sell new shares of stock to raise money, and the extra capital can be used to invest in new products, expand businesses, or pay off debt.
The third benefit of bull markets is that they help the economy grow. When stock prices are rising, companies have more money to invest and hire new employees. This increased economic activity can lead to even higher stock prices, creating a feedback loop that drives economic growth.
Finally, bull markets increase confidence. When stock prices are rising, people feel more confident about the future. This increased confidence can lead to even more investment and further economic growth.
The average bull market lasts about four years historically, but bull markets can last for much longer. The longest bull market in history lasted nearly eleven years, from October 1990 to March 2000.
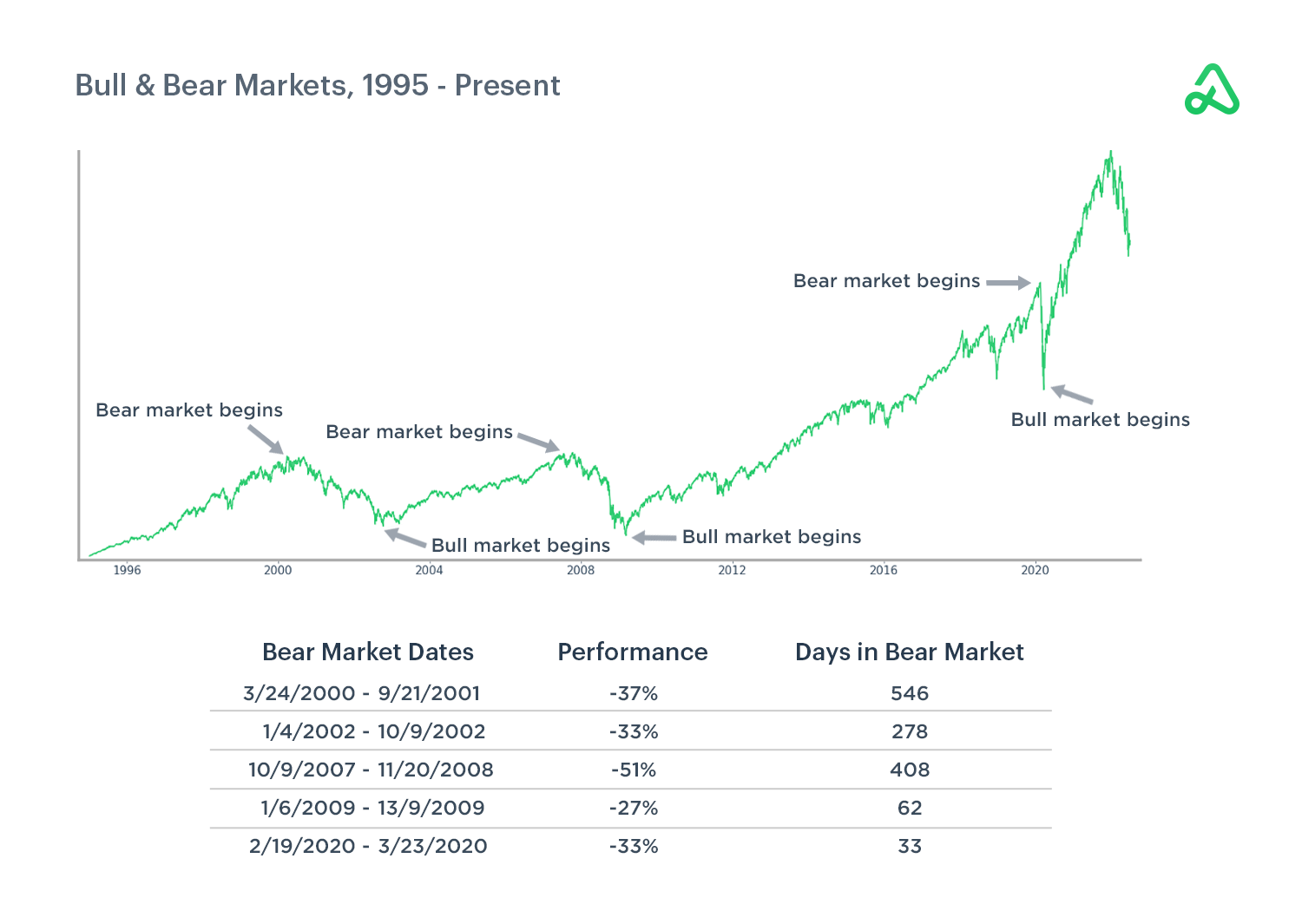
There are several signals that a bull market may be coming to an end:
The first signal that a bull market may be coming to an end is rising interest rates. When interest rates increase, borrowing money becomes more expensive for companies. This can lead to decreased investment and lower profits.
The second signal that a bull market may be coming to an end is slowing economic growth. People are less likely to invest in stocks when the economy slows down, decreasing demand and lower stock prices.
The third signal that a bull market may be ending is decreasing corporate profits. When companies start to make less money, their stock prices usually fall, leading to lower demand and further price decreases.
The fourth signal that a bull market may be ending is falling stock prices. When stock prices start to fall, it is often a sign that the bull market is ending.
Finally, when investors feel less confident about the future, they are less likely to invest in stocks. This can lead to decreased demand and lower stock prices.