


Covered Put is created when a trader feels that the stock price is going to remain range bound. It is the opposite of the moderately bullish covered call strategy. In order to create a covered put, you have to short a stock and short a stock and also short put options on the stock.
The put sold is generally at the money or slightly out of the money. The investor is moderately bearish on a stock and shorts it but will buy it back once it reaches a target price (the strike price he shorted the put option at). The trader who wrote the put option, is subjected to a very high risk if there is a dramatic rise in the stock price. As the stock price has no limit, the risk here is very high.
When to Use: If the investor is of the view that the markets are moderately bearish.
Risk: Unlimited if the price of the stock rises substantially.
Reward: Maximum is (Sale Price of the Stock – Strike Price) + Put Premium.
Breakeven: Sale Price of Stock + Put Premium.
Profit when: Premium Received - Commissions Paid.
Loss when: Price of Underlying - Sale Price of Underlying - Premium Received + Commissions Paid.
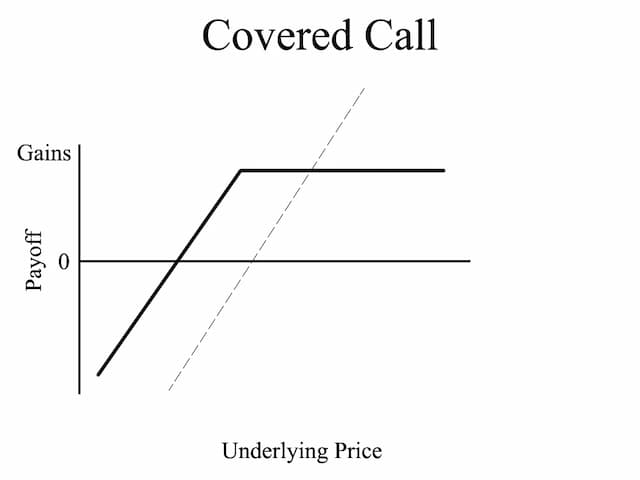
In the above figure, we have underlying price on the "X" or the horizontal axis and Payoff/profit on the "Y" or the vertical axis.
| Stock sold | Current Nifty index | 12000 |
|---|---|---|
| Put option shorted | Strike Price (Rs.) | 11900 |
| Received | Premium | 100 |
| Break Even Point (Rs.) (Strike Price + Premium) | 12100 |